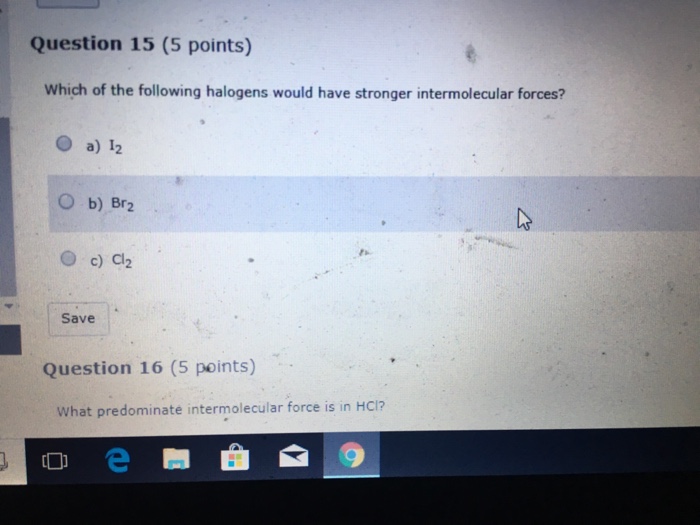
Which of the Following Halogens Would Have Stronger Intermolecular Forces
Larger molecules have larger electron clouds so you can expect the halogen with the larger diatomic molecule to exhibit the strongest London dispersion forces. And this is manifested by.
Solved Question 15 5 Points Which Of The Following Chegg Com
This is why at room temperature iodine which has the largest molecule is a solid bromine which is the next in line in terms of size is a liquid and fluorine and chlorine the smallest of the molecules are.

. So I2 has the. So it has stronger forces and higher boiling point. Leave a Reply Cancel reply.
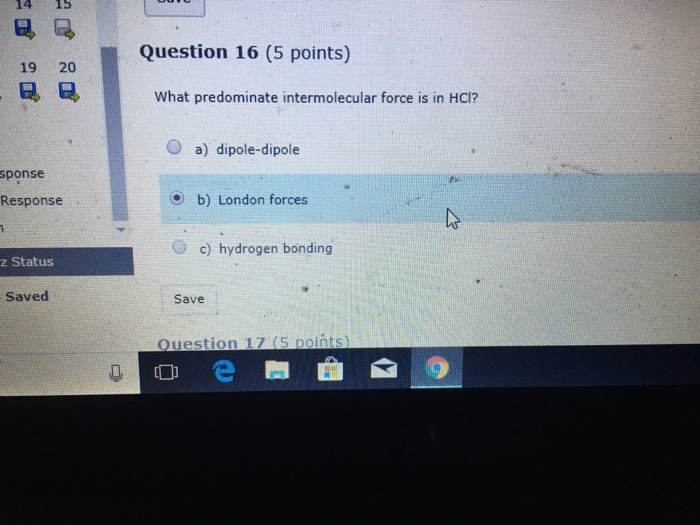
London dispersion forces affect boiling point. Br Cl I 2 2 2 Question 2 1 1. None of these have dipoles.
Well the halogens have dispersion forces as the only intermolecular force of attraction. Br 2 is a liquid and I 2 is a solid reflecting stronger attractive forces. Strengths of H-bonds are typically between 13 and 40 kJmole.
Name the intermolecular forces existing in the following liquids. Because larger hexane molecule has more places for attraction and greater polarizability than smaller ethane molecule. For example larger atoms have stronger London dispersion forces affecting them thus holding them together stronger increasing the energy required to pull them apart and thus the boiling temperature.
As hydrogen bonding is usually the strongest of the intermolecular forces one would expect the boiling points of these compounds to correlate with hydrogen bonding interactions present. Viscosity of a liquid arises due to strong intermolecular forces existing between the molecules. At room temperature the halogens with.
Hence ethanol would have a lower boiling point than 12-ethanediol but ethane and dimethyl ether would both have lower boiling points. Bigger molecules will have stronger London dispersion forces. The boiling point of a substance is proportional to the strength of its.
Br2 F2 I2 Cl2 Answer Higher boiling points will correspond to stronger intermolecular forces. None of these have hydrogen bonding. Further due to stronger forces hexane is a liquid while ethane is a gas at room temperature.
Your email address will not be published. Atoms or ionsIntermolecular forces are weak relative to intramolecular forces the forces which hold a molecule together. Is an exceptionally strong dipole-dipole force one of the three most electronegative elements F O or N must be covalently bonded to a hydrogen such as HF H2O NH3 CH3OH and CH3NH2.
F2 Cl2 Br2 I2. Which of the following halogens would have stronger intermolecular forces. List the following molecules in order of increasing boiling point.
Stronger the intermolecular forces greater is the viscosity. View Homework 3docx from CHEM 1806 at Barton Community College. Question 1 0 1 pts Which of the following halogens would have stronger intermolecular forces.
For example the halogens from smallest to largest. The physical state of hydrocarbons changes with an increased molecular mass. Outcome 8 DOK 1 Which of the following halogens would have stronger intermolecular forces.
An intermolecular force is an attractive force that arises between the positive components or protons of one molecule and the negative components or electrons of another molecule. Trends in observed melting and boiling points for the halogens clearly demonstrate this effect as seen in. F 2 and Cl 2 are gases at room temperature reflecting weaker attractive forces.
This occurs when compounds contain O-H N-H or F-H bonds. The only attractive force for nonpolar. A The boiling point of water in the Carpathian Mountains is greater than 100 C because of lower atmospheric pressure which results in increased intermolecular forces so it would take less time to boil the egg.
Various physical and chemical properties of a substance are dependent on this force. An intermolecular force IMF or secondary force is the force that mediates interaction between molecules including the electromagnetic forces of attraction or repulsion which act between atoms and other types of neighboring particles eg. Outcome 8 DOK 1 A Br2 B Cl2 C I2.
London Dispersion Forces induced dipole forces. 1 Liquid 2 Solid 3 Gel 4 Gas 5 NULL. Larger and heavier atoms and molecules exhibit stronger dispersion forces than do smaller and lighter atoms and molecules.
From strongest to weakest the intermolecular forces rank in the following way. Why should iodine be a solid. As the molecule X_2 gets bigger and the electron cloud correspondingly gets bigger with greater Z there should be a greater force of intermolecular interaction as the electron becomes more polarizable.
B The boiling point of water is always 100 C regardless of elevation so it would take the same amount of time to boil the egg. Go through the list above. Overcome the intermolecular forces The stronger the intermolecular force the more energy heat is required to undergo a phase change from solid to liquid to gas In the table above you can see that as the LDF increase with increasing molecular weight more energy is required to melt solidliquid and boil liquid gas the halogen.

Organic Chemistry Science Educational School Posters Organic Chemistry Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry
Strength Of Intermolecular Forces Psiberg
Solved Question 15 5 Points Which Of The Following Chegg Com
Comments
Post a Comment